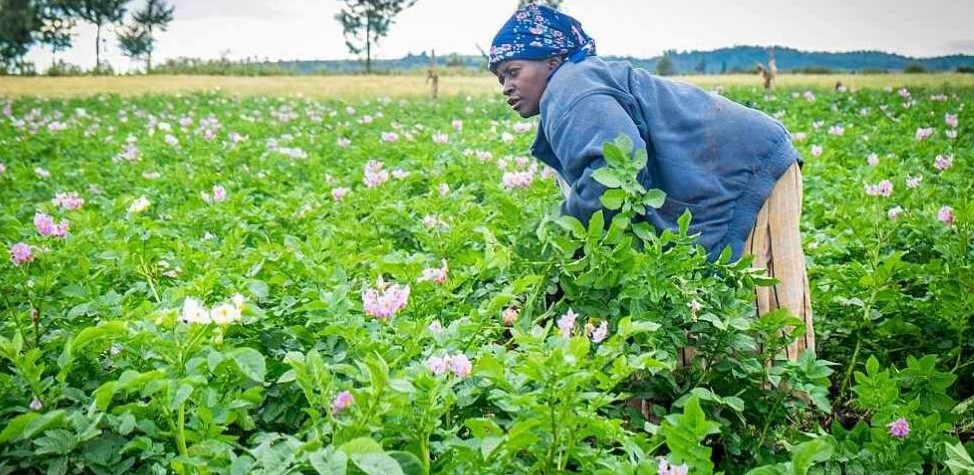
Food security is a critical issue, and Kenya, like many other countries, faces challenges in ensuring access to safe and nutritious food for its population. In this comprehensive blog post, we will explore the concept of food security, its various dimensions, the causes of food insecurity, and the specific context of food security policies in Kenya. By understanding these key aspects, we can uncover potential solutions and policy approaches to improve food security in Kenya.
Contents
- 1 Defining Food Security and Food Insecurity
- 2 Causes of Food Insecurity in Kenya
- 3 Types and Levels of Food Security
- 4 Context of Food Insecurity in Kenya
- 5 Components of Food Security Policies in Kenya
- 6 Solutions to Food Insecurity in Kenya
- 7 Importance of Food Security Policies
- 8 Current Food Security Policies in Kenya
- 9 Future Directions and Policy Recommendations
Defining Food Security and Food Insecurity
Food security refers to the availability, access, utilization, and stability of food that meets individuals’ dietary needs. It ensures that people have physical and economic access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food at all times. On the other hand, food insecurity means the lack of access to enough food for an active and healthy life, resulting in hunger, malnutrition, and other negative consequences.
Causes of Food Insecurity in Kenya
Food insecurity in Kenya stems from a combination of factors. Socio-economic challenges such as poverty, unemployment, and income inequality contribute significantly. Limited access to productive resources like land, water, and capital hinders agricultural productivity and food production. Climate change and environmental degradation pose additional threats, affecting agricultural yields and exacerbating food insecurity. Political instability, conflicts, and displacement also disrupt food access and distribution, particularly in certain regions.
Types and Levels of Food Security
Food security can be examined across four dimensions: availability, access, utilization, and stability. Availability refers to the quantity and quality of food produced, imported, and stored. Access focuses on people’s ability to obtain food through various means, including income, markets, and social safety nets. Utilization pertains to the utilization of food, ensuring proper nutrition and dietary diversity. Stability concerns the ability to sustain access to food over time, even in the face of shocks or disruptions.
Context of Food Insecurity in Kenya
Kenya faces specific challenges related to food insecurity. Vulnerable populations, such as smallholder farmers, pastoralists, and urban slum dwellers, are disproportionately affected. Limited access to markets, financial services, and agricultural technologies hinders agricultural productivity. Frequent droughts and erratic rainfall patterns, exacerbated by climate change, pose significant challenges to food production and livelihoods. Additionally, conflicts and displacement in certain regions disrupt food access and exacerbate food insecurity.
Components of Food Security Policies in Kenya
Effective food security policies in Kenya encompass various components. These include promoting sustainable agriculture practices, enhancing agricultural productivity, investing in irrigation and water management systems, supporting smallholder farmers through access to credit and improved inputs, strengthening market linkages and value chains, implementing social protection programs, and improving nutrition education and healthcare services.
Solutions to Food Insecurity in Kenya
Addressing food insecurity requires a multi-pronged approach. Key solutions include improving agricultural infrastructure, such as irrigation systems and storage facilities, to enhance productivity and reduce post-harvest losses. Supporting smallholder farmers through training, access to credit, and improved market access is vital. Strengthening social safety nets and nutrition programs can provide a buffer against shocks and ensure vulnerable populations have access to food. Diversifying income sources and promoting off-farm livelihood opportunities can enhance resilience and improve food security.
Importance of Food Security Policies
Food security policies play a crucial role in addressing food insecurity in Kenya. They provide a framework for coordinated action, resource allocation, and interventions to enhance food production, distribution, and access. These policies guide investments in agriculture, promote sustainable practices, and ensure that vulnerable populations have access to food and nutrition. They also create an enabling environment for private sector engagement and innovation, driving agricultural growth and development.
Current Food Security Policies in Kenya
Kenya has implemented several food security policies to address the challenges of food insecurity. The National Food and Nutrition Security Policy, the Agricultural Sector Transformation and Growth Strategy, and the Kenya Climate Smart Agriculture Implementation Framework are among the key policy frameworks. These policies emphasize sustainable agricultural practices, value chain development, social protection programs, and climate change adaptation and mitigation strategies.
Future Directions and Policy Recommendations
To improve food security in Kenya, policymakers should focus on strengthening the resilience of agricultural systems, promoting climate-smart agriculture, investing in agricultural research and technology, and enhancing market linkages for smallholder farmers. It is crucial to prioritize policies that empower vulnerable populations, promote gender equity, and address the root causes of food insecurity. Collaboration between government, civil society, and the private sector is vital for effective policy implementation and monitoring.
Conclusion
Ensuring food security in Kenya requires concerted efforts, policy interventions, and collaboration across various sectors. By understanding the complexities of food security, identifying the causes of food insecurity, and recognizing the importance of targeted policies, Kenya can make significant strides toward achieving sustainable food security. Through investments in agriculture, social protection programs, and climate change adaptation, Kenya can improve access to nutritious food, alleviate poverty, and enhance the overall well-being of its population.
We have a firm belief that every organization has a unique purpose only they can fulfil in this world. We work with you in organizing your resources to exploit opportunities so that you can fulfil your purpose and realize full potential. We build the capacity of people, processes and systems for organizational success and growth as well as nurturing a thriving ecosystem.
Ready to enhance your skills and boost your career? Explore our corporate training programs now and start your journey to success.






[…] Understanding Food Security: Definition, Causes of Food Insecurity, and Policy I… June 12, 2023 […]
[…] we will explore the transformative potential of these advancements in addressing global food security and environmental sustainability […]