Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Key Elements of Precision Agriculture
- 3 FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- 3.0.0.0.1 What exactly is precision agriculture?
- 3.0.0.0.2 How does GPS technology benefit precision agriculture?
- 3.0.0.0.3 How does precision agriculture contribute to environmental sustainability?
- 3.0.0.0.4 What role does artificial intelligence play in the future of precision agriculture?
- 3.0.0.0.5 How does blockchain enhance supply chain transparency in agriculture?
- 3.0.0.0.6 What are the benefits of using drone swarms for crop monitoring?
- 4 Conclusion
Introduction
In the realm of modern agriculture, precision agriculture stands out as a game-changer. This comprehensive article delves into the intricate world of precision agriculture, highlighting its multifaceted components, advantages, and its pivotal role in shaping the sustainable future of farming.
Unveiling Precision Agriculture
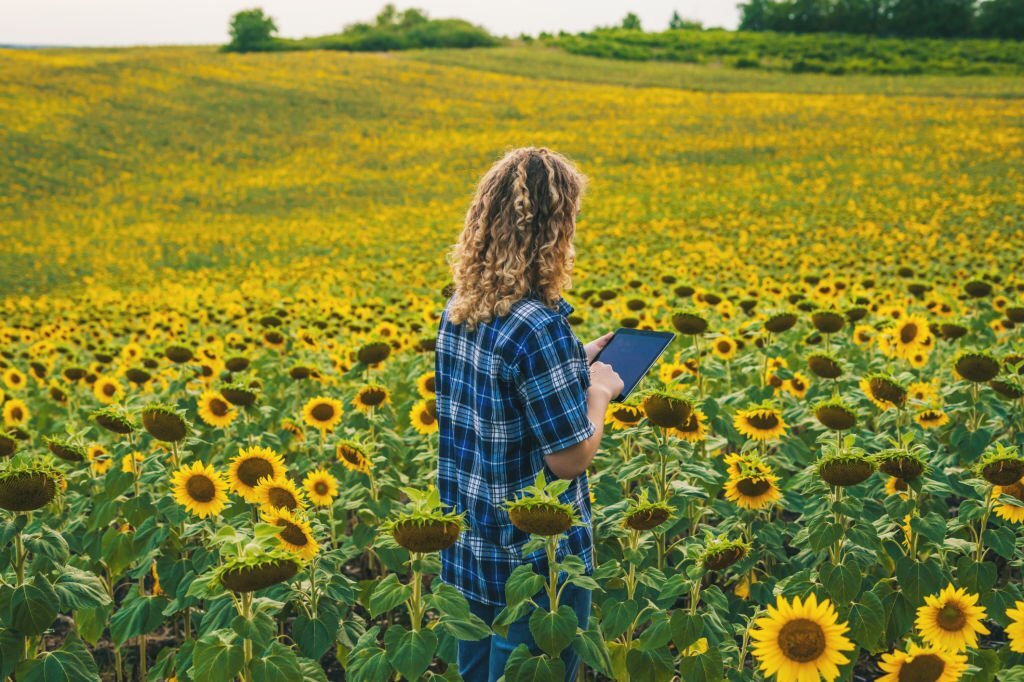
Precision agriculture, often referred to as smart farming, is a forward-thinking approach that harnesses cutting-edge technology to optimize various facets of farming operations. It’s all about meticulous resource management, including water, fertilizers, pesticides, and labor, with the aim of maximizing productivity while minimizing waste. At its core, precision agriculture relies on advanced technologies such as GPS, sensors, drones, and data analytics.
Read also: Agribusiness Trends: Navigating the Agricultural Landscape
Key Elements of Precision Agriculture
-
Data Gathering and Analysis
At the heart of precision agriculture lies data-driven decision-making. The modern farmer collects an abundance of data from their fields, encompassing vital metrics like soil moisture, temperature, and crop health. This data undergoes rigorous analysis, empowering farmers to make well-informed choices regarding planting, irrigation, and pest control.
Transitionally, this data serves as the guiding star in the vast ocean of agriculture, steering farmers towards higher productivity. They harness data from their fields, tapping into sensors that monitor soil moisture, temperature, and crop health. This wealth of data is then meticulously analyzed to make informed decisions, be it for planting strategies, efficient irrigation, or targeted pest control.
-
GPS Technology
The Global Positioning System (GPS) takes center stage in precision agriculture. It empowers farmers to meticulously map their fields and track the movements of farming equipment with unparalleled accuracy. This technology ensures that every crop is planted, irrigated, and harvested with utmost precision.
Transitionally, GPS technology has been nothing short of revolutionary in the world of agriculture. It offers farmers precise coordinates for their fields, enabling accurate field mapping and equipment tracking. The outcome? Every square inch of the field is optimized for productivity.
-
Automation and Robotics
The integration of robotic technology into agriculture has revolutionized labor-intensive tasks. Automated machinery handles activities like seeding, weeding, and harvesting with unmatched precision, effectively reducing the need for manual labor.
The dawn of automation and robotics has significantly streamlined farming operations. These advanced machines work with precision levels that surpass human capabilities. As a result, efficiency soars, and labor costs plummet.
The Advantages of Precision Agriculture
-
Enhanced Productivity
When it comes to achieving higher yields, precision agriculture proves to be a valuable ally. Meticulous resource management and process optimization result in remarkable productivity gains.
Transitionally, enhanced productivity is the hallmark of precision agriculture. By carefully allocating resources and fine-tuning processes, farmers witness significant yield improvements.


-
Cost Reduction
Efficient resource utilization doesn’t just boost productivity; it also translates into substantial cost savings. Accurate resource allocation results in reduced operational expenses, a financially prudent and environmentally responsible choice.
Efficient resource allocation translates into not just higher productivity but also substantial cost savings. By accurately distributing resources, farmers reduce the need for excessive fertilizers and pesticides, saving money and curbing environmental impact.
-
Environmental Sustainability
Precision agriculture inherently champions environmental sustainability. Minimized chemical use, water conservation, and reduced soil erosion contribute to a healthier ecosystem.
Transitionally, precision agriculture champions the cause of environmental sustainability. By minimizing chemical usage and conserving water, it mitigates the negative impacts of farming on the environment. Reduced soil erosion further enhances the ecological footprint.
-
Data-Driven Decision-Making
Access to real-time data empowers farmers to make informed decisions promptly. They can respond swiftly to changing weather conditions or pest infestations, preventing potential crop loss.
Data-driven decision-making serves as the bedrock of precision agriculture. Real-time data offers invaluable insights, allowing farmers to take timely actions, mitigating the risks associated with unpredictable weather or sudden pest outbreaks.
The Future Prospects of Precision Agriculture
The future of farming unequivocally resides in precision agriculture. As technology continues to advance, we anticipate the emergence of even more sophisticated tools and techniques in this field. Here are some exciting prospects:
-
Artificial Intelligence Integration
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to revolutionize precision agriculture. AI algorithms will analyze data at unprecedented speeds, providing actionable insights and predictions for optimal farm management.


Transitionally, the integration of artificial intelligence represents the next frontier in precision agriculture. AI’s ability to process vast datasets rapidly will usher in a new era of data-driven decision-making, enabling farmers to anticipate challenges and seize opportunities more effectively.
-
Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain technology can be seamlessly integrated into precision agriculture to ensure transparency in the food supply chain. Consumers will gain access to detailed information about the origin and quality of the produce they purchase.
The adoption of blockchain technology in agriculture enhances the transparency and traceability of the food supply chain. It provides consumers with a window into the journey of their food from farm to table, fostering trust and accountability.
-
Drone Swarms for Crop Monitoring
The use of drone swarms equipped with cameras and sensors will become increasingly prevalent for real-time crop monitoring. This technology can swiftly identify early signs of disease or nutrient deficiency, allowing for immediate intervention.
Transitionally, the deployment of drone swarms for crop monitoring is on the rise. These swarms, armed with advanced sensors and cameras, offer farmers a bird’s-eye view of their fields, enabling them to detect and address issues promptly.
Click here to subscribe for free article notification
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What exactly is precision agriculture?
It is an innovative farming approach that deploys technology to optimize various facets of farming operations, including resource management, planting, and pest control.


How does GPS technology benefit precision agriculture?
GPS technology empowers farmers to meticulously map their fields and track farming equipment with unparalleled accuracy, ensuring precise planting and harvesting.
How does precision agriculture contribute to environmental sustainability?
It minimizes chemical use, conserves water, and reduces soil erosion, promoting a healthier ecosystem.
What role does artificial intelligence play in the future of precision agriculture?
Artificial intelligence will analyze data at unprecedented speeds, offering insights and predictions for optimal farm management.
How does blockchain enhance supply chain transparency in agriculture?
Blockchain technology ensures transparent tracking of produce, providing consumers with origin and quality information.
What are the benefits of using drone swarms for crop monitoring?
Drone swarms equipped with sensors swiftly detect early signs of disease or nutrient deficiency, enabling prompt intervention and improved crop health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, precision agriculture is set to reshape the future of farming. With its data-driven approach, advanced technology integration, and numerous benefits, it offers a sustainable and efficient path forward for agriculture. Transitionally, farmers who embrace this not only enhance their yields and profitability but also contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly future for our planet. Start embracing precision agriculture by enrolling in one of the courses on IRES institute. Embracing this cutting-edge approach is essential for staying ahead in the ever-evolving landscape of agriculture, ensuring that we not only keep pace but lead the way toward a brighter and more sustainable future for farming worldwide.
About Me
I am an experienced digital marketing professional dedicated to achieving online success. With a strong background in SEO, social media, content creation, graphic design, video editing, content marketing, and social listening, I bring a comprehensive skill set to help businesses thrive in the digital landscape.








Comment here